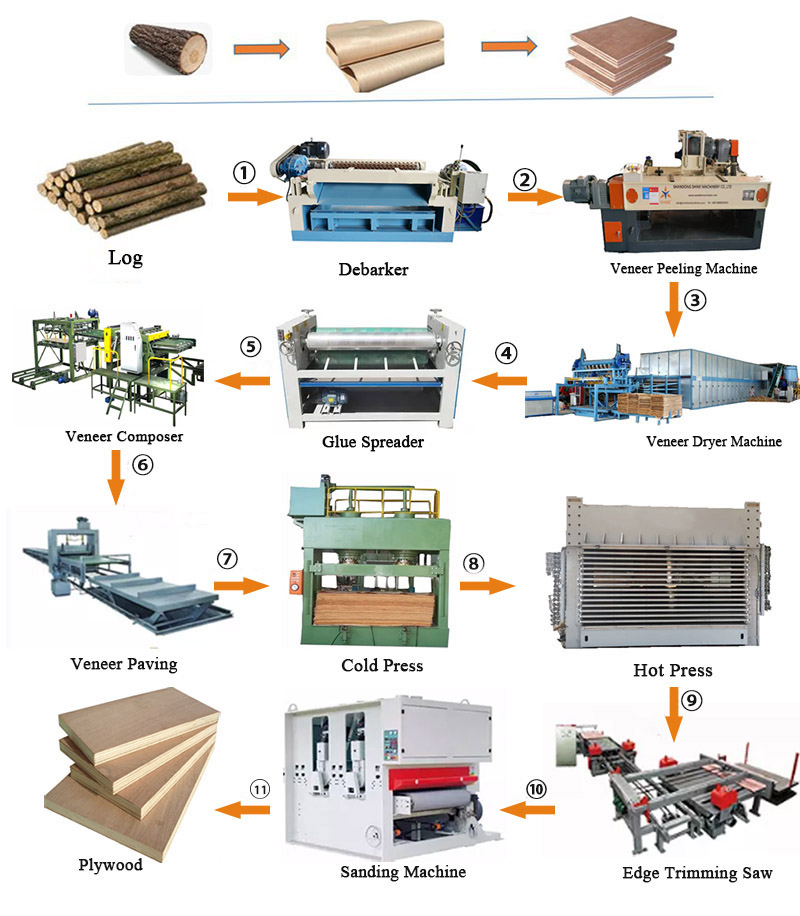
Plywood production process
The production process of plywood is a multi-step process involving raw material processing, veneer production, gluing and pressing, and post-processing. Here are the main production processes:
1. Log processing
Cut: Cut logs into lengths suitable for peeling or planing (usually 2.6 meters or customized sizes).
Debarking: Remove bark to reduce the impact of impurities on subsequent processes.
Cooking and softening (optional): Soak or cook logs (temperature about 60-80℃) to soften wood fibers for peeling.
2. Veneer production
Pearl cutting (main process):
Fix the softened logs on the peeling machine and rotate to cut out continuous veneers (thickness 0.1-4mm).
Planing (special needs):
For wood with high texture requirements (such as decorative panels), planing is used to obtain veneers with straight grain or special patterns.
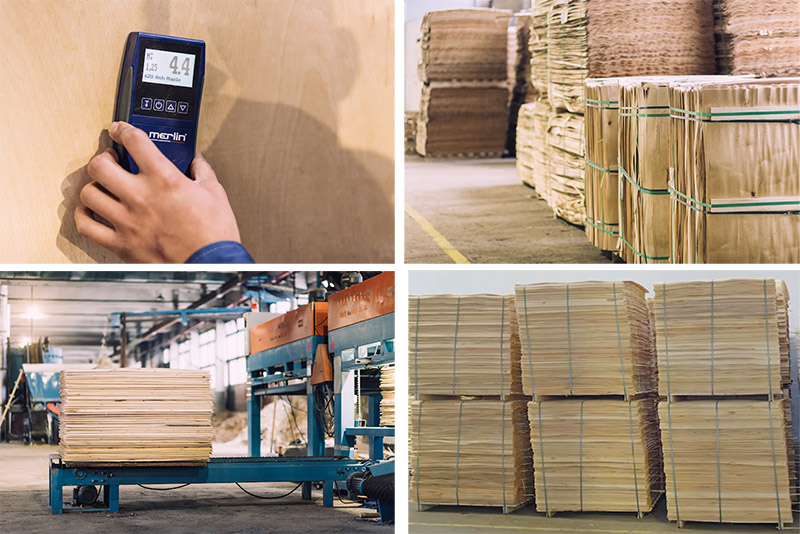
The moisture content of the veneer is reduced to 6-12% through a veneer dryer (temperature 70-120℃) to prevent deformation after gluing.
3. Veneer finishing
Sorting and repairing:
Remove defective veneers such as cracks and wormholes, and repair small holes or cracks.
Gluing:
Apply adhesive (usually urea-formaldehyde resin, phenolic resin or environmentally friendly glue) evenly on the surface of the veneer, with an amount of about 100-300g/m².
4. Assembly (overlapping)
Structural design:
Overlap veneers (odd number of layers, such as 3 layers, 5 layers) according to the principle of "vertical wood grain of adjacent layers" to ensure balanced strength.
Symmetrical arrangement:
Use high-quality veneer for the surface layer, and thicker or low-cost wood for the core layer.
5. Hot pressing
Pre-pressing (optional):
Preliminary pressure fixation of the veneer to reduce misalignment during hot pressing.
Hot pressing:
In a hot press (temperature 110-140℃, pressure 1.0-1.5MPa, time 1-1.5 minutes/mm thickness), the adhesive is cured to form a stable board.
6. Post-processing
Cooling and curing:
Naturally cool and stand for 24-48 hours to release internal stress and stabilize the size.
Trimming and sanding:
Cut into standard size (such as 1220×2440mm), sand the surface until it is flat and smooth.
Grading and inspection:
Grade strength, moisture content, and appearance according to national standards (such as GB/T 9846).
7. Special treatment (optional)
Veneer treatment: additional decorative layer (such as veneer, melamine impregnated paper).
Functional treatment: moisture-proof (phenolic glue), fireproof (flame retardant immersion), anti-corrosion (chemical treatment), etc.
Key control points
Veneer quality: uniform thickness and no defects.
Adhesive selection: environmental protection (such as E0/E1 grade), water resistance.
Hot pressing parameters: temperature, pressure, and time must match the type of glue and thickness.
Moisture content control: avoid warping or cracking of the board.
Application areas: building formwork, furniture manufacturing, packaging boxes, ships, etc.